
How to use Qt WebAssembly – The Complete Guide with demo
Hey, welcome back to another blog post. Today we’re going to talk about the new Qt WebAssembly. This post will […]
Join us at Qt C++ Warsaw Meetup - 21.08.2025
Sign up for free!
Modern C++ (C++17 and later) is great in finance where performance and reliability matter. C++ code is compiled directly into machine code, no virtual machine or garbage collection, low latency and very fast. This is why C++ is the “language of choice for latency critical systems” and one of the dominant production quality languages — from trading engines to high-frequency trading (HFT) platforms where microsecond delays can mean millions of dollars lost. C++ gives full control over memory and hardware, so you can tune performance (e.g. custom network drivers). And with built-in multithreading (std::thread, std::async) you can use multiple CPU cores efficiently.
In quantitative finance where precision matters these are very valuable. In addition to its object oriented programming and generic programming roots, C++ also supports functional programming patterns which can simplify some data transformations in quantitative code.
Now, let’s take a closer look at some of the C++ features and design patterns that make it particularly effective in this domain. Or, if you’re already planning a project and looking for help with high-performance financial software in modern C++, Scythe Studio can help – contact us.
C++ has several critical advantages that make it very attractive for the financial sector:
C++ code is compiled into machine code, no virtual machine or interpreter overhead. This means maximum performance — a key feature for HFT systems where every microsecond counts. This execution time advantage puts C++ among the top production quality languages in finance.
Efficient memory management, no garbage collection pauses and control over system resources down to the hardware level makes C++ unbeatable in latency sensitive environments. Avoiding memory leaks and having control through tools like smart pointers allows financial programmers to build robust systems with minimal runtime overhead.
Financial applications often require optimization of network communications, disk I/O, memory allocation and even CPU cache usage. C++ gives you full control over these layers. This control allows you to build systems tailored to the hardware, better scalability and predictability than higher level languages. Raw pointers are still present in performance critical paths but are often replaced with modern features to enable safe implementation.
Modern C++ standards have native support for multithreading (std::thread, std::async) and parallel programming (std::execution). In finance where massive simulations (e.g. Monte Carlo) or real-time data processing are common the ability to fully use multi-core and multi-processor environments is crucial. Concepts like task-based concurrency make concurrent code more reliable and reduce the error prone nature of older threading approaches.
Since C++11 the language has got tools to make code safer, more expressive and easier to maintain:
All these modern features added in recent C++ standards have moved the language towards a modern perspective on software development, balancing power and safety. Many financial institutions use C++ for mission critical systems and many financial firms are investing in its evolution.

Despite many advantages C++ also has drawbacks, especially in finance:
C++ is a complex language, combining procedural, object oriented and generic programming paradigms. Mastering it takes years and mistakes (especially memory and concurrency related) can lead to serious security and stability risks. Many programmers coming from higher level languages will find C++ challenging due to its complex source code structure and manual resource handling.
Writing and maintaining C++ code — especially secure and highly optimized code — takes more time than scripting languages like Python. Debugging, profiling and code optimization are often supported by test cases but still require significant effort. Writing clean code is key to keep large financial applications maintainable and readable.
In dynamic areas like fintech startups or research groups where rapid iteration is important languages like Python or JavaScript are more often used in software development for startups. C++ is better suited for production environments than for rapid experimentation. But with tools like pybind11 C++ systems can support faster prototyping and testing.

C++ is used in many financial systems. Key examples are:
| Aspect | C++ | Python | Java | Rust |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | 🟢 Very High | 🔴 Low | 🟡 Good | 🟢 Very High |
| Ease of Use | 🔴 Difficult | 🟢 Very Easy | 🟡 Moderate | 🔴 Difficult |
| Financial Industry Popularity | 🟢 Very High | 🟢 High | 🟡 Moderate | 🟡 Growing |
| Memory Management | Manual/Smart Pointers | Automatic (GC) | Automatic (GC) | Ownership Model |
| Libraries and Tools | Very Rich | Very Rich | Rich | Growing |
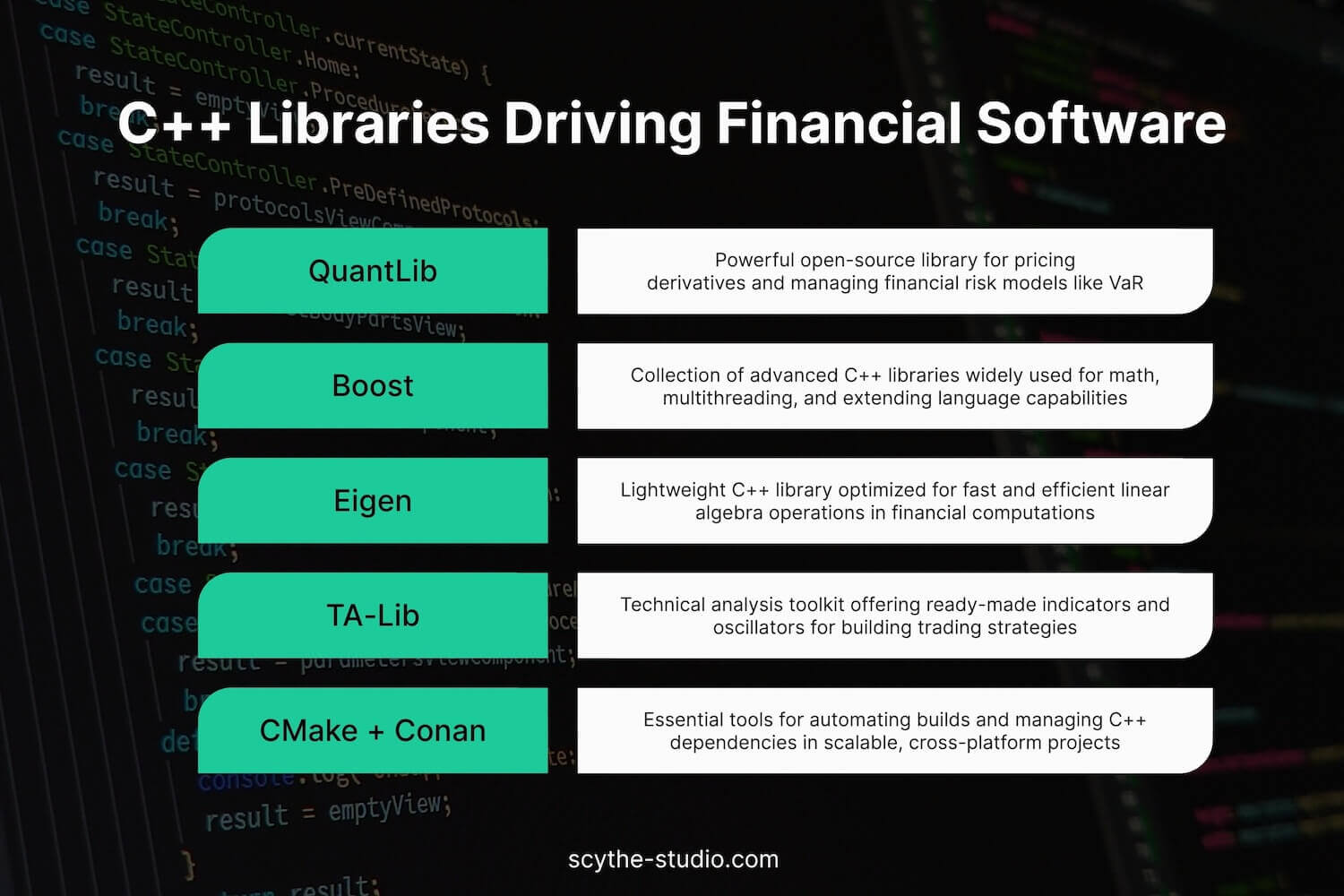
In financial practice many C++ libraries are used. The most important are:
Thanks to these libraries and tools C++ developers in financial institutions can develop and maintain production systems faster and more reliable. They are the foundation, enabling access to performant and scalable solutions in demanding environments.
Several trends are shaping the role of C++ and related technologies in the financial sector. Although some ask “is C++ still popular?” the language continues to evolve and remains a cornerstone in production finance systems.
Rust, offering similar performance to C++ but without common memory pitfalls (e.g., avoiding classic C++ data races through its ownership model) is being explored in financial systems. Rust’s strict compiler checks aim to enable safe code and reduce memory leaks and undefined behavior possible in C++. Some firms are experimenting with rewriting parts of existing financial applications in Rust, although the C language roots of many systems and the wide availability of C++ knowledge means C++ still dominates production systems.
Many modern systems integrate a high-performance C++ core with Python or R interfaces for data analysis. Tools like pybind11 make it easy to create bindings between C++ and Python. This hybrid model is particularly useful for financial firms wanting to combine C++’s performance with Python’s agility for analysis and visualization. These mixed-language systems improve developer productivity, allowing to write clean code for both backend and scripting layers and make it easier to experiment with test cases around core engines.
This allows numerical algorithms or simulation engines written in C++ to be called directly from Python scripts, speeding up prototyping and integration with the broader data science ecosystem. Similar integration techniques exist for Java (via JNI) and microservices architectures, enabling flexible and scalable financial solutions. These architectural patterns reflect the modern way financial applications are designed and maintained. In parallel, many firms reduce in-house development costs through C++ outsourcing, engaging external teams for performance-critical components while retaining core quantitative logic internally.
Although Python is the primary language for AI/ML research, C++ plays a key role underneath — especially in high-performance ML engines, inference libraries and GPU acceleration layers. For example, the core components of TensorFlow and PyTorch are written in C++. These engines are used for fraud detection, portfolio optimization and market prediction, often involving large datasets and real-time inference — areas where C++’s performance and control matter.
C++’s role in machine learning in computational finance reflects its growing presence in solving mathematical problems beyond traditional models. This is part of a broader convergence of computer science, numerical analysis and finance — areas where C++ is a foundational programming language.
In summary C++ is the foundation of high-performance financial applications across trading, risk and analytics. Despite new languages like Rust, its unique strengths in system-level control, performance and flexibility keep it relevant in finance. If you are learning or advancing in this space, the practical book by Daniel Hanson is highly recommended as it shows how to solve mathematical problems with a modern C approach and full access to C++ features.
Let's face it? It is a challenge to get top Qt QML developers on board. Help yourself and start the collaboration with Scythe Studio - real experts in Qt C++ framework.
Discover our capabilities
Hey, welcome back to another blog post. Today we’re going to talk about the new Qt WebAssembly. This post will […]

Users of embedded devices – from industrial controllers to consumer electronics – are often unaware of hidden vulnerabilities that threaten […]

Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are becoming more and more important in embedded devices – from home appliances to medical equipment […]