
Secure Boot and Firmware Protection in Embedded Systems
Users of embedded devices – from industrial controllers to consumer electronics – are often unaware of hidden vulnerabilities that threaten […]
Join us at Qt C++ Warsaw Meetup - 21.08.2025
Sign up for free!
Experience a world where manufacturing operations are well-connected, machines can interact with each other and identify faults before they take place, that is the concept of Industry 4.0. As the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) progresses and advances in cyber-physical systems and smart factories continue to arise, industries have been rapidly transforming themselves from what we used to know.
This blog post will explore how this fourth industrial revolution has completely changed sectors such as supply chain management through IoT devices which enable production flows smoother than ever before.
It delves into understanding exactly what effects Industry 4.0 possesses on businesses all over the globe. Both its good aspects along with the obstacles it faces by taking advantage of technology like the Internet of Things at play here. Organizations that stay ahead in terms of these developments increase their market standing resulting from harnessing this potential accordingly for assured success eventually.
We will also shortly look into the topic of software development technologies used to code smart devices and other types of machinery that you can find in a smart factory.
The fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, has altered the way businesses operate and progress by integrating digital technology with cyber-physical systems, IoT devices, and more. In some sense, it is similar to the third industrial revolution and previous events as it completely changed the way industry operates.
However this shift is significantly different from its predecessors in that it goes beyond improving the efficiency of manufacturing processes or supply chains – it creates entire smart factories! The first industrial revolution began at the end of the 1700s to early 1800s when labor was replaced by waterpower steam engines combined with machine tools.
Then came along the second industrial revolution which leveraged production processes and the third industrial revolution which used electronic components with computers for automating certain activities linked to production from the mid-1900s onwards.
The crux behind the current wave lies within the Internet of Things (IoT). Networked physical gadgets connected to the web holding potential access to storing/sharing data inclusive of those coming from remote sensors. An example would be the modern agriculture industry where IoT sensors allow effective production of foodstuffs on a larger scale. Often without a need to leave the home.

Industry 4.0 includes applications in different sectors such as aforementioned agriculture, oil and gas, heavy machinery, robotics, automotive, smart cities, and many many more. The easiest explanation here would be that it makes sense to introduce wherever there is a need to improve business processes.
The real power of the Internet of Things becomes evident when we witness its applications in real-world scenarios:
Use case: Automotive Manufacturing
Leading automotive manufacturers like BMW and Tesla utilize IoT systems to create fully connected assembly lines. Each station in the assembly process communicates with the others in real-time, ensuring smooth operations. This kind of smart manufacturing is applicable to all types of factories. Wherever there are manufacturing processes to be optimized.
Use case: E-commerce and Retail
Companies like Amazon use IoT devices to optimize warehousing. Sensors track inventory levels, and smart shelves can notify managers when stock is running low or when items are misplaced. Robots, guided by IoT systems, move goods around the warehouse efficiently, preparing them for shipment or restocking, ensuring that the supply chain runs seamlessly.
In the nearby from our office in Warsaw, there is a huge bakery with a warehouse being one giant freezer. Humans can not enter there. Everything is operated by robots controlled by a network of connected devices.
To properly understand terminology such as Industry 4.0 or IoT systems we have to first know what components such systems consist of. What technologies make regular electronic devices smart?
Every component within the IoT framework relies heavily on software. From the simplest temperature sensors to the most complex robotic machinery, they all operate based on code that dictates their function and behavior.
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Software: This is a staple in industrial machinery. PLCs have been around even before the term ‘IoT’ was coined. They control machinery based on input conditions, and in Industry 4.0, their software has evolved to not only control but also communicate with other devices, collect data, and make decisions.
High-level Software: This includes desktop and mobile applications that act as interfaces between humans and machines. They gather, display, and analyze data coming from various IoT devices. They also enable users to input commands, adjust settings, visualize outcomes, and ensure IoT device management.
Custom software development plays a pivotal role here. While there are many out-of-the-box solutions available, having custom software ensures that the system is tailored to specific industrial needs, allowing seamless integration with other components and maximizing efficiency. Moreover, it enables adaptability – a crucial aspect in the ever-evolving landscape of Industry 4.0.
Embedded development sits at the intersection of hardware and software in the IoT ecosystem. It focuses on creating specialized software for devices that aren’t typical computers. This ensures that the electronics in these devices can perform dedicated functions or tasks without the need for broad computing resources.
In essence, embedded development ensures that the right hardware, paired with purpose-built software, is at the heart of every IoT device, making them both functional and intelligent.
Big Data refers to the vast volumes of IoT data collected daily. Through sophisticated analytics, industries extract meaningful insights from this data, optimizing processes and predicting trends. As IoT devices multiply, so does the importance of effectively managing and leveraging this ever-growing data reservoir.
In Industry 4.0, artificial intelligence powers advanced analytics of data from the Internet of Things. Through machine learning, systems autonomously adapt and optimize processes, bringing unparalleled efficiency and innovation to modern industries.
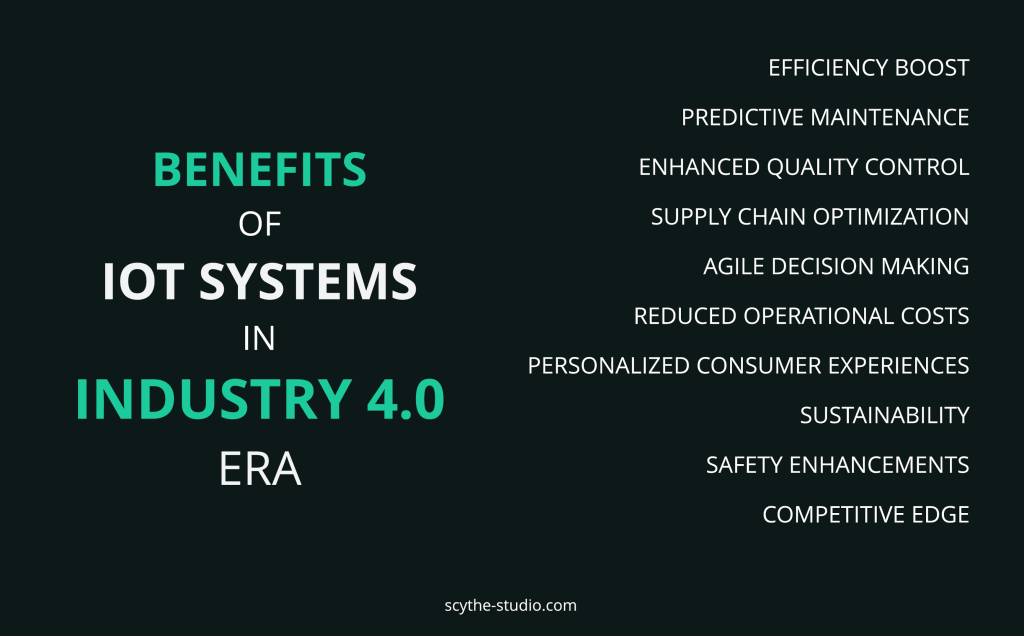
The integration of smart devices is reshaping the supply chain and therefore the business landscape. As Industry 4.0 advances, companies leveraging these technologies are experiencing transformative benefits across various operational facets.
Efficiency Boost: Industry 4.0 introduces smart factories where machinery and equipment can operate autonomously, leading to faster production cycles and reduced downtime.
Predictive Maintenance: Through data analytics, businesses can anticipate machinery faults before they occur, significantly reducing maintenance costs and unexpected operational halts.
Enhanced Quality Control: Smart manufacturing systems continually monitor product quality, ensuring consistent outputs and reducing defects.
Supply Chain Optimization: Digital transformation allows for real-time tracking of materials and products, leading to streamlined supply chains and reduced inventory costs.
Agile Decision Making: With continuous data flow from IoT devices, businesses can make more informed decisions quickly, adapting to market changes efficiently.
Reduced Operational Costs: Automated systems in smart factories often lead to reduced labor costs and more efficient use of resources.
Personalized Consumer Experiences: Industry 4.0 allows for more tailored product offerings based on real-time consumer data, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Eco-Factor: Smart systems optimize energy consumption and reduce waste, aligning businesses with green initiatives and sustainability goals.
Safety Enhancements: Autonomous systems can operate in hazardous environments, reducing workplace accidents and ensuring employee safety.
Competitive Edge: Embracing digital transformation positions businesses at the forefront of their industries, granting them a distinct competitive advantage in the market.
Starting an IoT project? It’s good to know the tech tools of the trade. Different sectors have their favorites, with some software solutions being more popular than others. Knowing what’s in demand can help set your project on the right path and keep it current with the times.
The choice of an operating system in Industry 4.0 largely depends on the device running the software:
Microcontrollers: For the most basic devices, often there’s no operating system in place. Sometimes, a real-time operating system (RTOS) might be employed, ensuring immediate responses to changes or inputs.
Embedded and Desktop Linux: Depending on the application’s requirements, many industrial IoT devices opt for Linux – either in its embedded or desktop form. It’s versatile, open-source, and well-suited for various IoT applications.
Windows and Windows Embedded: Despite the rise of Linux, Windows remains a significant player, especially in industries where devices are developed using C#. Thanks to the widespread popularity of desktop Windows and C# as a primary Microsoft programming language, it’s a go-to choice for many. However, it may be the issue in some cases that Windows requires to get a license for each distributed OS copy.
Android and iOS: Consumer IoT devices often are controllers and accessed through mobile apps. The situation is the same in the case of IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things). Smartphones and tablets are mobile and easy to get, so why not monitor your smart factory from your pocket?
Whichever OS is chosen, the Qt Framework – a popular C++ framework for software development, stands out as a robust tool, capable of managing and integrating these varied operating systems, ensuring smooth application development and deployment. We will introduce this solution in a minute.
In the world of Industry 4.0 and IoT, the choice of programming technology is pivotal to ensuring efficiency, performance, and scalability. Here are some of the frontrunners:
C: A bedrock of embedded systems, C remains a popular choice for many IoT devices owing to its performance and direct system resource access.
C++: Building on the foundation of C, C++ offers object-oriented features. It’s performant and meshes seamlessly with embedded platforms. Given its efficiency, it’s also a preferred choice for machine learning applications.
Python: Known for its simplicity and readability, Python has gained traction in the IoT world. Its wide range of libraries makes it ideal for data analytics, processing, and machine learning.
C#: Particularly prevalent in devices that run on Windows or where Microsoft’s ecosystem is dominant, C# provides a robust platform for developing IoT applications.
Emerging Choices: While less common, newer languages like Carbon, Dart (notably for Flutter development), and Rust are gaining momentum. They offer unique features that can be beneficial for specific IoT scenarios.
Lastly, the Qt Framework deserves special mention. This comprehensive tool facilitates the development of applications across various platforms, including those mentioned above, ensuring interoperability and a unified development experience.
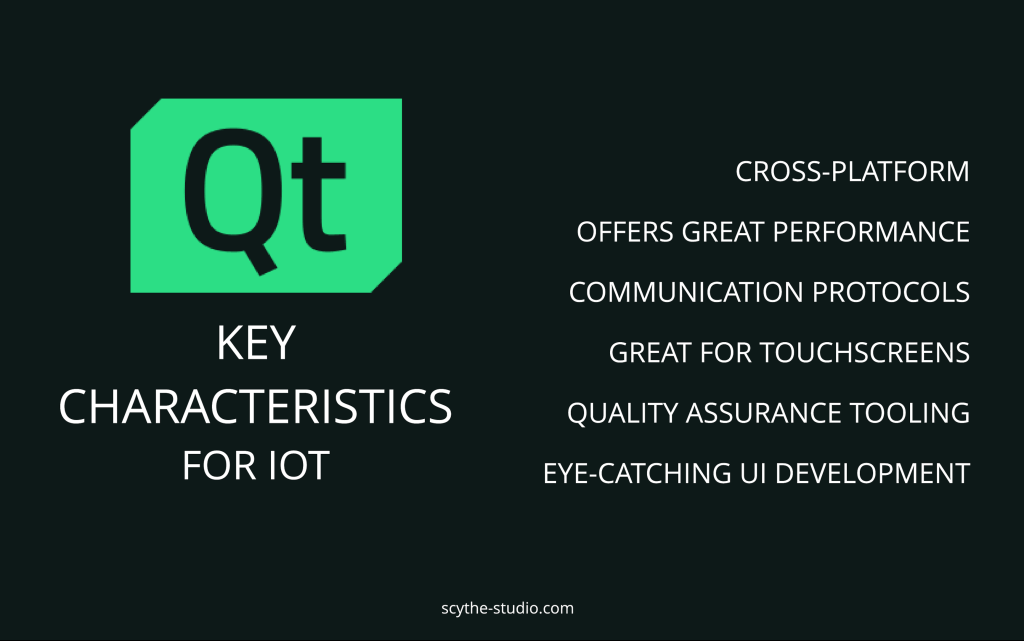
Qt framework is used in a wide range of projects supporting modern digital transformation processes. It serves as a solid base for IoT technology. There are still many aspects of the fourth industrial revolution that you may want to learn, so let’s not focus on the Qt framework anymore. If you want to learn more about it see this website about our Qt QML development.
Diving into the realm of IoT and Industry 4.0 can seem daunting, but with a structured approach, your journey can be streamlined and efficient. Here’s a five-step roadmap:
Start by understanding your primary goals. What problems are you aiming to solve? Whether it’s enhancing automation, streamlining operations, harnessing data for insightful analytics, or implementing predictive maintenance, pinpointing your objectives from the outset is vital. It will not only give clarity but also set the tone for subsequent stages.
Before making any concrete decisions, it’s imperative to involve all relevant stakeholders. These could be team members, managers, experts, or end-users whose input will influence the project’s trajectory. Collaborative discussions can shed light on challenges, and opportunities, and provide a holistic view, ensuring the project aligns with the larger organizational vision.
This involves identifying the best software and hardware technologies that align with your objectives. Whether you’re considering microcontrollers, sensors, or high-end machinery, the right tools matter. Remember, tools like the Qt framework can aid in unifying software development across devices.
This stage encompasses UX/UI designing, system architecture planning, and establishing network communication. Holding intensive interviews with stakeholders and industry experts is essential to crafting effective user cases and designing a seamless user interface. Integration with existing systems is also paramount. It’s worth noting that for those seeking professional guidance in these domains, Scythe Studio offers specialized services in IoT project development and UX/UI designing.
Once the groundwork is laid, develop a Proof of Concept. This phase allows you to test your ideas in a real-world scenario, ensuring that the solution is viable before a full-scale rollout.
Think about the workforce to handle the project. Hiring in-house specialists may be a reasonable choice to develop your next IoT project in case you already have a knowledge how what this project looks like. However, it’s also possible that your staff do not possess the required skills or simply have time to handle the task.
Outsourcing specialists is not as expensive as it seems. If you go with near-shoring you do not have to pay for vacations, workplace organization, training, administration, and social benefits of outsourced specialists. Just ensure that you start cooperating with actual experts.
By adhering to this approach, you’ll be well on your way to harnessing the transformative power of IoT and Industry 4.0.
The dawn of Industry 4.0 heralds a transformative era in the industrial landscape, underpinned by the might of the Internet of Things (IoT). As machines become smarter and more interconnected, they open up opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and growth across various sectors, from manufacturing to agriculture.
Delving into the technological backbone of this revolution, software emerges as the linchpin, driving the operations of diverse IoT devices. Whether it’s microcontrollers or advanced machines, the choice of operating systems, programming languages, and frameworks like the Qt framework plays a pivotal role in realizing the potential of these smart systems.
To truly harness the benefits of Industry 4.0, a strategic approach to IoT project initiation is imperative. This involves clear goal-setting, inclusive stakeholder discussions, astute technology assessments, meticulous project planning, and the eventual creation of a proof of concept.
In essence, the integration of smart systems in business operations isn’t just a trend; it’s a critical evolution. As industries worldwide adapt to this new paradigm, it’s vital for business leaders to consider the immense possibilities IoT offers. Optimize your supply chains, enhance processes, and drive forward by ushering in the IoT era. The future awaits!
Let's face it? It is a challenge to get top Qt QML developers on board. Help yourself and start the collaboration with Scythe Studio - real experts in Qt C++ framework.
Discover our capabilities
Users of embedded devices – from industrial controllers to consumer electronics – are often unaware of hidden vulnerabilities that threaten […]

Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are becoming more and more important in embedded devices – from home appliances to medical equipment […]
Technical managers in the embedded space often face a classic challenge: integrating industrial communication protocols into modern applications. One such […]